Ion Exchange (IEX): How Do They Work And What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages
Spheres of sulphonated synthetic resin.. yes we will discuss ion exchange resins (IEX) which are used for various water treatment applications like water softening, water demineralization and processes as desinfection, deionization and dealkalization. In this blog we will go into the following themes;
- What is an ion exchanger?
- How does an ion exchanger work?
- What are the advantages of an ion exchanger?
- What are the disadvantages of ion exchanger?
- What can be removed with ion exchanger?
- Ion exchange and quality standards
What is an ion exchanger?
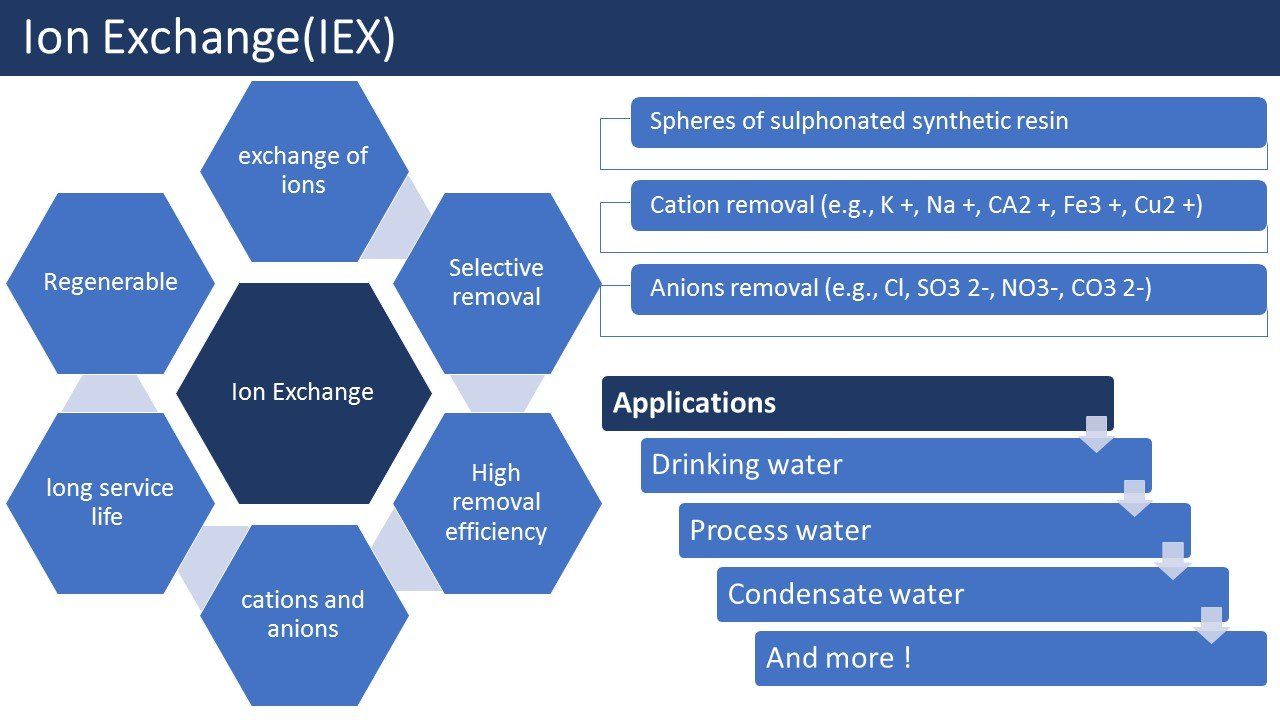
Ion exchangers (IEX) are spheres of sulphonated synthetic resin that can take ions from liquid, water, process water, condensate water, swimming pool water) by changing them out against other ions. The liquid will flow over a with beads filled with ion exchanger resin column. The beads are solid and this is often referred to as adsorption resin.
There are also non-ionic resins, these are capable of removing organic contaminants such as for example trichlorethylene and tetrachlorethylene.
What do the dictionaries say about ion exchange;
"The process of reciprocal transfer of ions between a solution and a resin or other suitable solid."
Source: https://www.dictionary.com/browse/ion-exchange
"A reversible chemical reaction between an insoluble solid and a solution during which ions may be interchanged, used in water softening and in the separation of radioactive isotopes."
Source: https://www.yourdictionary.com/ion-exchange
How does an ion exchanger work?
A ion exchanger works on the basis of exchange of ions (as the name implies).A little bit of background information about what an ion is; an ion is an electric charged atom or molecule that is present in, for example, water as K + Na +,CA 2+ or Cl-, positive ions are called cations and negative ions anions. If negative ions are removed, then an anion exchanger is used, if it is desired to remove positive ions then one can use a cation exchanger. In some cases you can do both in one system, this is called a mixed bed(mixed bed system).After some time an ion exchanger is saturated, it can be regenerated with a regenerant usually this is an acid or a base. The resin particles have often a uniform particle size. A uniform particle size has a number of advantages over a large spreard of the particle size of the resin particles. Benefits include; better water quality, better separation layered beds and mixed beds, higher efficiency and greater mechanical stability.
What are the advantages of an ion exchanger?
- Selective removal is possible by choosing the right ion exchanger
- High removal efficiency is possible for cations and anions
- Regeneration of the bed gives a very long service life (disadvantage of acid and base required = costs)
- Ion exchangers can also work well with low water pressure
What are the disadvantages of an ion exchanger?
- Sensitive to pollution, think, for example, of suspended particles
- Resin can be sensitive for oxidizing substances
- Cost of acids and bases for regeneration
- Often a pre-purification step is needed such as aeration of the water, sedimentation and sand filtration.
- Efficacy can be reduced due to fouling, by for example mineral scaling or surface clogging
- Disposal costs of the acids and bases used for regeneration
What can be removed with an ion exchanger?
With an ion exchanger, cations can be removed (e.g., K +, Na +, CA2 +, Fe3 +, Cu2 +, Mg +)and anions can be removed (e.g., Cl, SO3 2-, NO3-, CO3 2-) from for example drinking water, spring water, process water and condensate water. A lot of elements from the
periodic system of elements in ionic form and substances like
PFAS can be removed with this technique.
Ion exchange and quality standards
Follow the link for a separate blog about this topic
"ion exchange and quality standards".
In this blog we have given a basic knowledge about the meaning and effects of the purification technology ion exchanger, we have discussed here what an ion exchanger is, how it does work, what the advantages and disadvantages of ion exchangers are and what can be removed with an ion exchanger and from what kind of liquids. Also read our other and future blogs about various purification techniques